Disk Usage on the Linux
Check Disk Usage on the Linux with du Command is a crucial aspect of maintaining a healthy Linux system. When storage starts to fill up, identifying which files or directories are consuming the most space can save time and prevent disruptions. The du (disk usage) command is an indispensable tool for this purpose, providing detailed insights into disk usage at the file and directory level.
Introduction
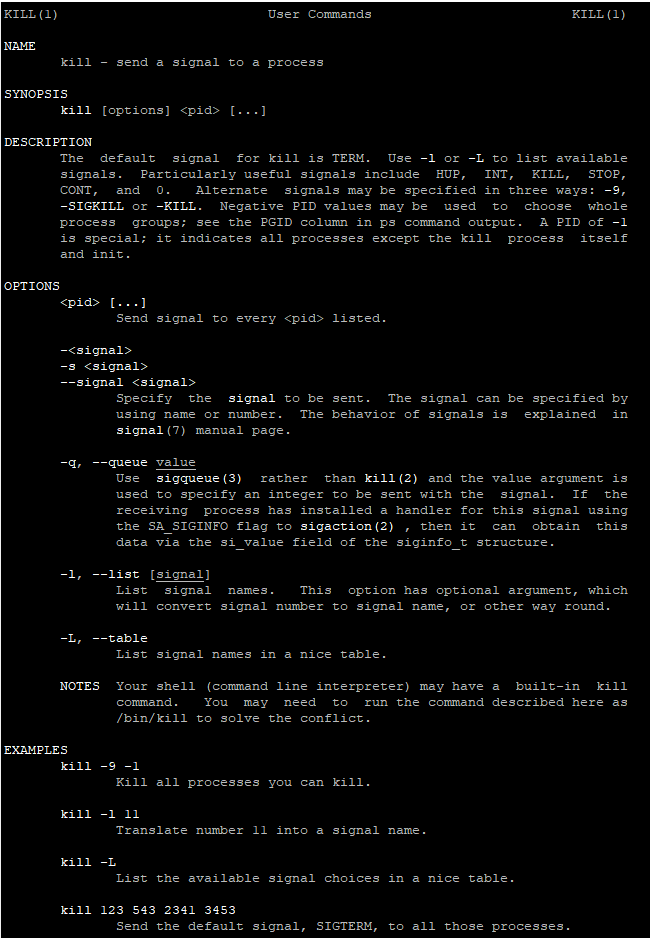
The du – disk usage command displays the amount of disk space used by files and directories on Linux systems. By default, it shows the disk usage of each directory and subdirectory within the current directory.
Basic du Syntax
du [OPTION]... [FILE]...Commonly Used Options
Here are some of the most commonly used options with the du command:
-aor--all: Includes both files and directories in the output.-hor--human-readable: Displays sizes in human-readable format (e.g., K, M, G).-sor--summarize: Displays only the total for each argument.-cor--total: Displays a grand total of the disk usage found by the other arguments.--max-depth=N: Limits the output to directories (and files) at most N levels deep.-dor--depth=N: Similar to--max-depth=N, shows the total for directories up to N levels deep.--exclude=PATTERN: Excludes files that match the given pattern.
Basic Examples of du command
- To display the disk usage in a human-readable format:
du -h- To display only the total disk usage of the current directory:
du -sh- To include all files in the output:
du -ah- To limit the depth of the directories shown in the output to two levels:
du --max-depth=2- To display a grand total at the end of the output:
du -ch
- To exclude files that match a specific pattern:
du --exclude='*.log'- Displays disk usage of files and directories and summarize the total size of each argument:
du -skh *Advanced Usage and Tips
- Analyzing Large Directories: Combine
duwith other commands likesortandheadto find the largest directories:
du -ah /path/to/directory | sort -rh | head -n 10- To see the memory usage of directories within a folder and sort them by size, you can use the
du(disk usage) command combined withsort:
du -h --max-depth=1 /path/to/folder | sort -hrExplanation
du -h --max-depth=1 /path/to/folder:dustands for “disk usage.”-hmakes the output human-readable (e.g., in K, M, G for kilobytes, megabytes, and gigabytes).--max-depth=1limits the command to only look at the top-level directories within/path/to/folder.
sort -hr:sortsorts the output.-hsorts by human-readable numbers.-rsorts in reverse order (i.e., from largest to smallest).
- To check the memory usage in the current directory and sort by size:
du -h --max-depth=1 . | sort -hr
This command will provide a list of directories and their sizes, sorted from largest to smallest.
Other Examples
A very efficient way to check disk usage is the ncdu application. You can check it at the link.