Process Management and kill Command
The Ubuntu kill command is a fundamental tool for managing processes in a Linux environment. Whether you’re troubleshooting unresponsive applications or managing system resources, understanding how to use the kill command effectively is essential for any Linux user or system administrator.
Introduction
This guide will walk you through the basics of the kill command, its various options, and practical examples to help you master process control in Ubuntu.
Understanding the Kill Command
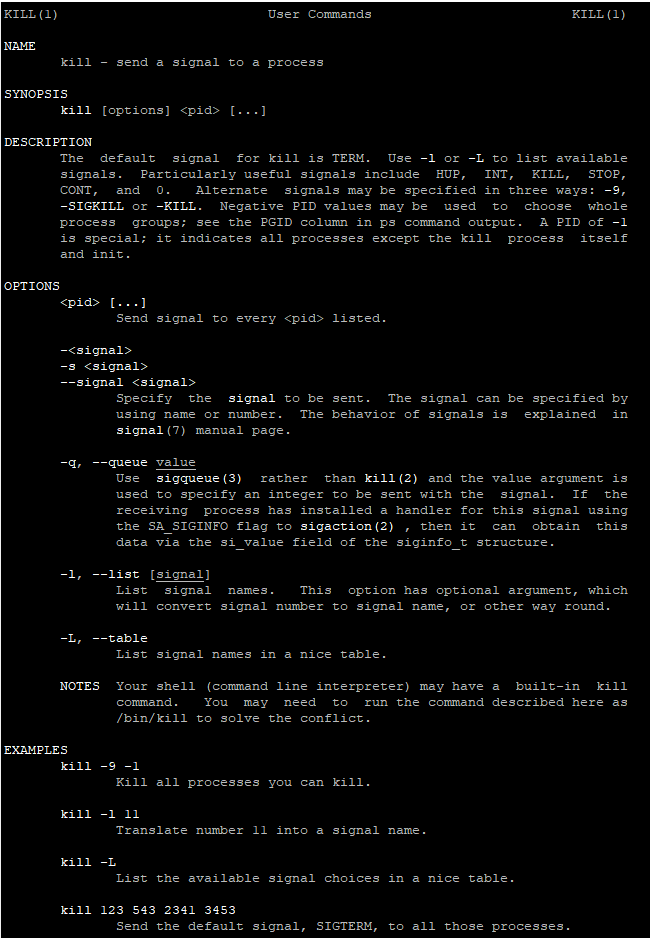
The kill command in Ubuntu is used to send signals to processes, usually to terminate them. Each process running on your system has a unique Process ID (PID), and using the kill command, you can send specific signals to these processes to control their behavior.
Basic Syntax
kill [OPTIONS] PIDOPTIONS: Various options or signals to specify the type of action to perform.PID: The Process ID of the process you want to target.
Common Signals
Here are some of the most commonly used signals with the kill command:
SIGTERM (15): The default signal that requests a process to terminate gracefully.SIGKILL (9): Forces a process to terminate immediately without cleanup.SIGHUP (1): Hangs up the process, often used to reload configuration files.
Examples of Using the Kill Command
- Terminate a Process Gracefully:
# This command sends the SIGTERM signal to the process with PID 1234.
kill 1234- Force Terminate a Process:
# Using the -9 option sends the SIGKILL signal, forcing the process to terminate immediately.
kill -9 1234
- Reload a Process Configuration
# This command sends the SIGHUP signal to the process, causing it to reload its configuration without stopping.
kill -1 1234Finding Process IDs
Before you can use the kill command, you need to know the PID of the process you want to manage. You can find PIDs using the ps or top commands.
Example of ps command:
# This command lists all processes matching process_name.
ps aux | grep process_nameAdvanced Kill Command Options
- Kill All Instances of a Process:
# The killall command terminates all processes with the specified name.
killall process_name- Send a Custom Signal:
# Replace SIGNAL_NAME with the desired signal (e.g., HUP, TERM) to send a custom signal to a process.
kill -s SIGNAL_NAME PIDYou can find more examples of kill command at this post.