FortiGate as a DHCP Server
Configuring FortiGate as a DHCP server allows network administrators to easily manage IP address distribution within their network. In this article, we will explore how to configure FortiGate as a DHCP server both via the GUI and CLI, including some advanced configuration options.
A DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server is used to dynamically assign IP addresses to devices on a network. FortiGate firewalls, aside from their security capabilities, can also act as DHCP servers.
DHCP GUI Configuration
To configure FortiGate as a DHCP server through the graphical user interface (GUI), follow these steps:
Step 1: Access the FortiGate Web Interface
- Open a web browser and enter the IP address of the FortiGate device.
- Log in using your administrator credentials.
Step 2: Navigate to DHCP Server Settings:
- Go to Network > Interfaces.
- Select the interface where you want to enable the DHCP server (e.g., internal interface or LAN interface).
- Click on the Edit button for that interface.
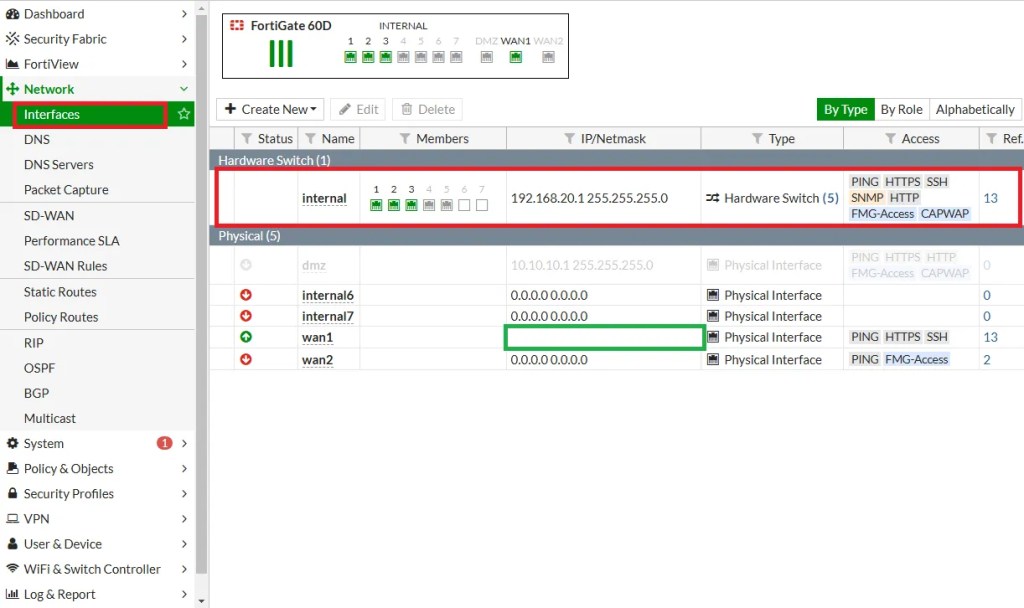
Step 3: Enable DHCP Server
- In the Edit Interface window, scroll down to the DHCP Server section.
- Check the Enable DHCP Server box to activate the DHCP server on that interface.
Step 4: Configure DHCP Server Settings:
- DHCP Range: Specify the range of IP addresses that the server will assign to clients (e.g., 192.168.20.110 to 192.168.20.210).
- Subnet Mask: Set the subnet mask for the DHCP clients (e.g., 255.255.255.0).
- Gateway IP: Define the default gateway IP address for the clients (usually the IP address of the FortiGate interface).
- DNS Server: Optionally, configure the DNS servers that the clients should use. In my case I am using Google DNS Servers.

If you need to make IP ADress Reservation you can add MAC Adress of device and IP Adress in the “MAC Reservatrion” Table:

Step 5: Save the Configuration:
- After entering the necessary information, click OK to save the settings.
DHCP CLI Configuration
For administrators who prefer the command-line interface (CLI) or need to automate the configuration, setting up a DHCP server via CLI is also straightforward.
Step 1: Access the FortiGate CLI
- You can access the CLI through the console or SSH by connecting to the FortiGate device.
Step 2: Enable the DHCP Server on an Interface
Use the following command to configure the DHCP server on a specific interface (e.g., internal):
fgt-remote1 # config system dhcp server
fgt-remote1 (server) # edit 1
fgt-remote1 (1) # get
id : 1
status : enable
lease-time : 604800
mac-acl-default-action: assign
forticlient-on-net-status: enable
dns-service : specify
wifi-ac1 : 0.0.0.0
wifi-ac2 : 0.0.0.0
wifi-ac3 : 0.0.0.0
ntp-service : specify
domain :
wins-server1 : 0.0.0.0
wins-server2 : 0.0.0.0
default-gateway : 192.168.20.1
next-server : 0.0.0.0
netmask : 255.255.255.0
interface : internal
ip-range:
== [ 1 ]
id: 1
timezone-option : default
tftp-server :
filename :
options:
server-type : regular
conflicted-ip-timeout: 1800
auto-configuration : enable
ddns-update : disable
vci-match : disable
exclude-range:
reserved-address:
dns-server1 : 8.8.8.8
dns-server2 : 8.8.4.4
dns-server3 : 0.0.0.0
ntp-server1 : 0.0.0.0
ntp-server2 : 0.0.0.0
ntp-server3 : 0.0.0.0
fgt-remote1 (1) #
In this configuration:
- interface: The network interface where the DHCP server is enabled (e.g.,
internal). - lease-time: The lease time for IP addresses.
- subnet: The network address and subnet mask.
- range-start and range-end: The start and end of the IP address range that the DHCP server will assign to clients.
- default-gateway: The default gateway for clients.
- dns-server1 and dns-server2: DNS server addresses for clients.
Step 3: Verify DHCP Server Configuration
After configuring the DHCP server, you can verify the settings with the following command: show system dhcp server
fgt-remote1 # show system dhcp server
config system dhcp server
edit 1
set default-gateway 192.168.20.1
set netmask 255.255.255.0
set interface "internal"
config ip-range
edit 1
set start-ip 192.168.20.110
set end-ip 192.168.20.210
next
end
set timezone-option default
set dns-server1 8.8.8.8
set dns-server2 8.8.4.4
next
end
Conclusion
Configuring FortiGate as a DHCP server, either via the GUI or CLI, is a simple yet powerful way to manage IP address allocation for your network devices. By following the steps outlined above, you can easily set up a DHCP server, customize the IP address range, and apply advanced options like static IP mapping, TFTP server configuration, and DHCP relay. The flexibility offered by FortiGate allows you to fine-tune your DHCP settings to meet the specific needs of your network.
In next article we will write about DHCP special atributes. You can check my other FortiGate post on this link.














