Packet Capture
Packet capture on FortiGate firewalls is an essential tool for network administrators looking to diagnose issues and monitor network traffic. FortiGate offers packet capture functionality through both the Command Line Interface (CLI) and Graphical User Interface (GUI), each with unique advantages.
Packet Capture from CLI
The CLI allows for detailed and flexible packet capture commands, useful for advanced troubleshooting. To start a packet capture in CLI, use the diag sniffer packet <interface> <filter> <level> command. Here’s a basic example:
diagnose sniffer packet <interface> '<filter>' <verbosity> <count> <timestamp> <frame size>Parameters Explanation:
<interface>:- Specifies the network interface on which to capture packets (e.g.,
port1,wan1, oranyfor all interfaces). - Example:
wan1captures only packets on thewan1interface.
- Specifies the network interface on which to capture packets (e.g.,
<filter>:- This is a BPF (Berkeley Packet Filter) filter expression to limit captured traffic. It follows the same syntax as a filter in Wireshark or
tcpdump, letting you specify conditions like IP addresses, protocols, or ports. - Example:
'host 192.168.1.10 and port 80'captures traffic only to or from IP192.168.1.10on port 80.
- This is a BPF (Berkeley Packet Filter) filter expression to limit captured traffic. It follows the same syntax as a filter in Wireshark or
<verbosity>:- Controls the level of detail in the capture output. It ranges from
1to6.1: Displays only basic packet headers (minimal detail).4: Shows full packet details (recommended for in-depth troubleshooting) and interface name.6: Includes debug-level information (very verbose, often used for debugging).
- Example:
4for detailed packet information and ingress and egress interfaces.
- Controls the level of detail in the capture output. It ranges from
<count>:- Sets the maximum number of packets to capture before stopping.
- Example:
100captures only 100 packets and then stops.
<timestamp>:- Controls the display format of timestamps.
0: No timestamp.1: Unix timestamp in seconds.- a: prints absolute timestamp
- Example:
1for Unix timestamps.
- Controls the display format of timestamps.
<frame size>:- Sets the maximum size of each captured packet. This truncates packets beyond the specified size, capturing only the headers or a portion of the payload if needed.
- Example:
100captures the first 100 bytes of each packet.
Packet Capture from CLI – Example 1
diagnose sniffer packet any 'host 192.168.1.10' 4In this command, any indicates all interfaces, host specifies a targeted IP, and 4 sets the verbosity level. Results display real-time packets with rich detail, helping pinpoint issues like latency, dropped packets, and unexpected traffic patterns.
Packet Capture from CLI – Example 2
diagnose sniffer packet any 'host 192.168.1.10' 4 100 1 100Explanation: This command captures packets on all interfaces (any), filtered for IP 192.168.1.10. It uses verbosity level 4 for detailed information, captures up to 100 packets, includes Unix timestamps (1), and limits packet size to 100 bytes.
To capture to a file for later analysis, use:
diag sniffer packet <interface> 'filter' <level> file /path/filename.pcapPacket Capture from GUI
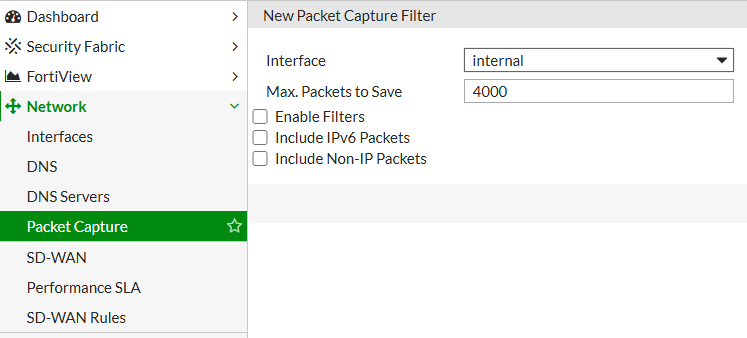
The GUI provides a more accessible interface for administrators unfamiliar with CLI commands. Go to Network > Packet Capture, select the interface, apply filters, and start the capture. The GUI option is ideal for quick captures and allows for saving and downloading captures in .pcap format, compatible with Wireshark for in-depth analysis.